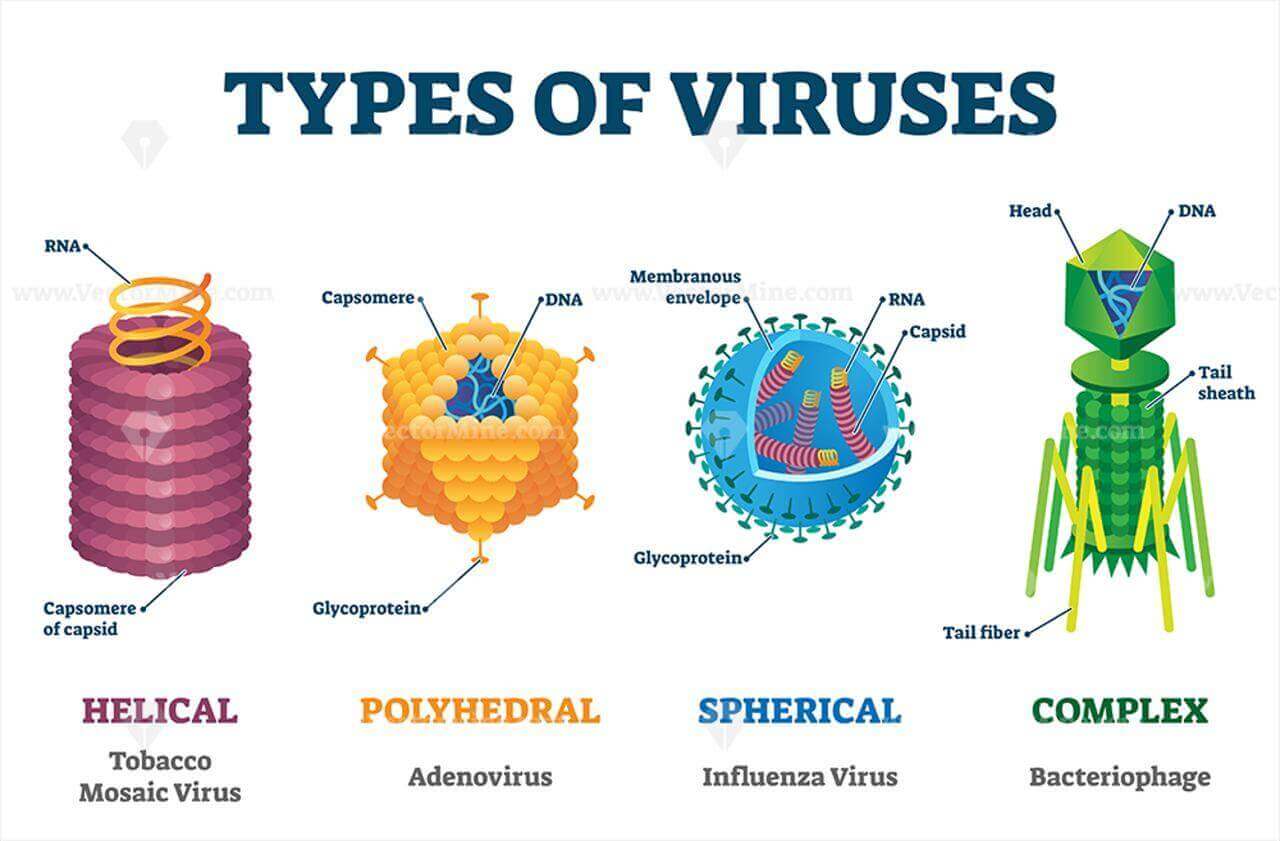
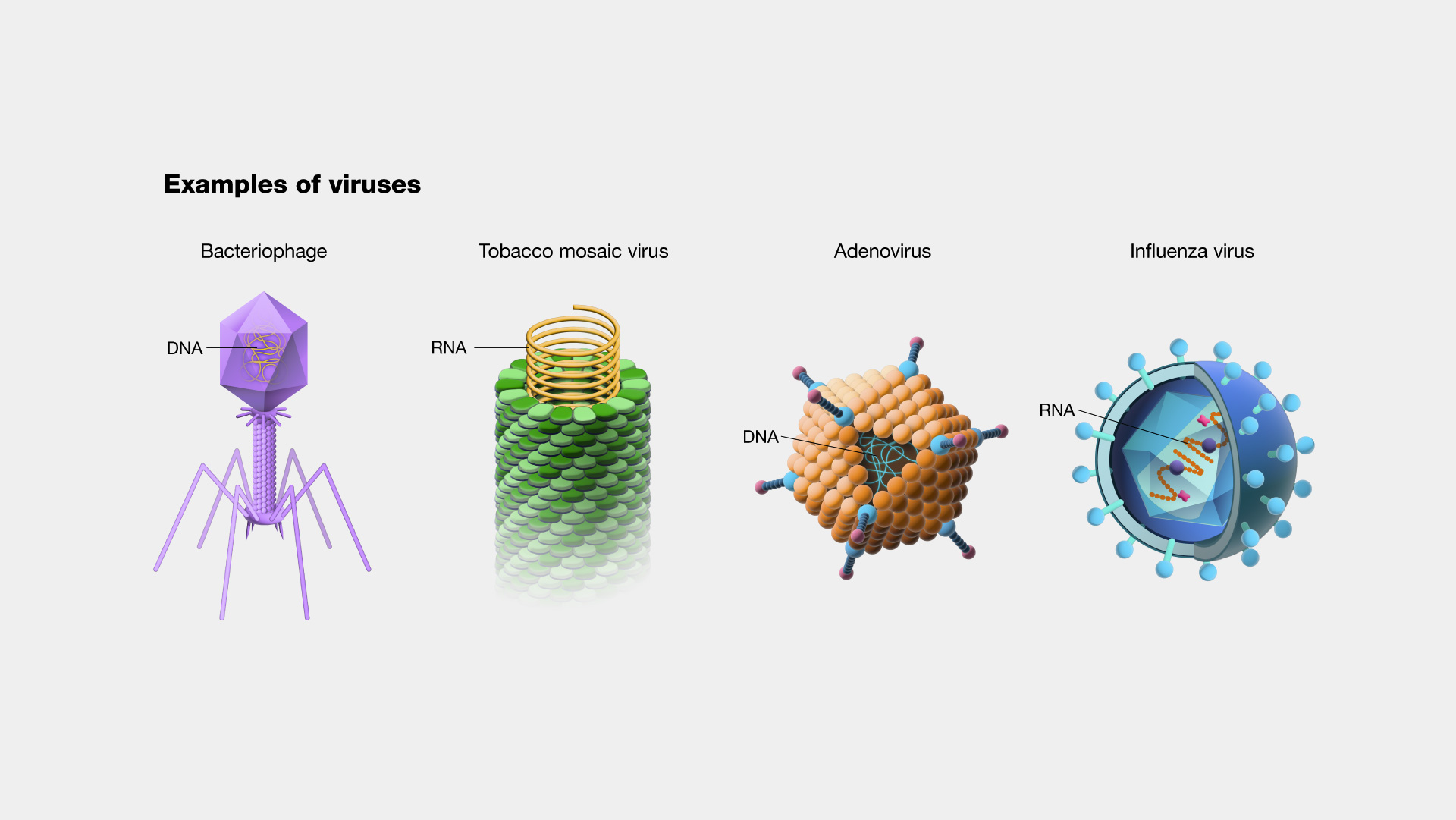
Images of DNAウイルス

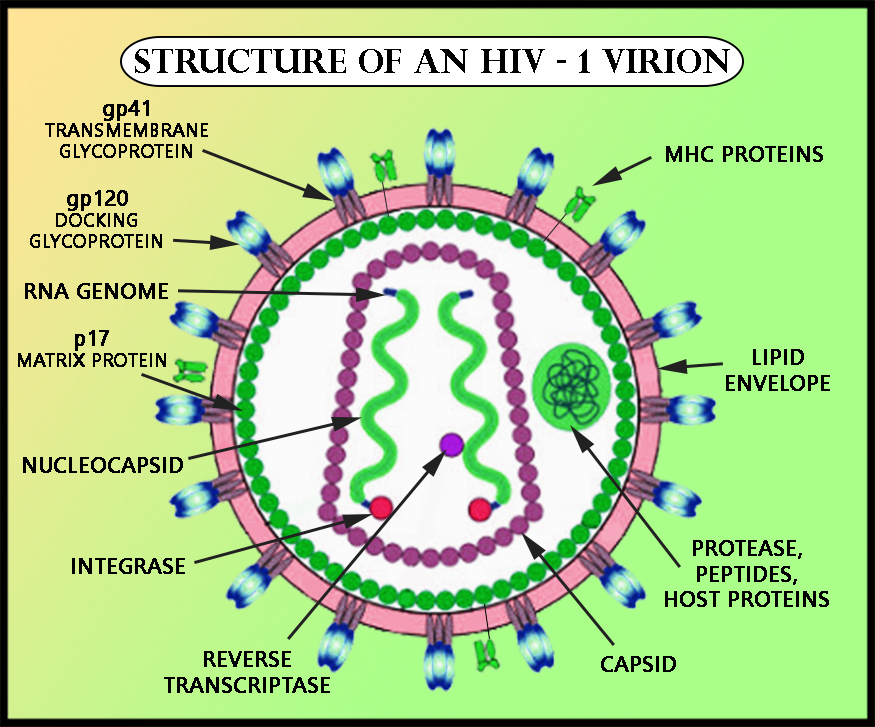
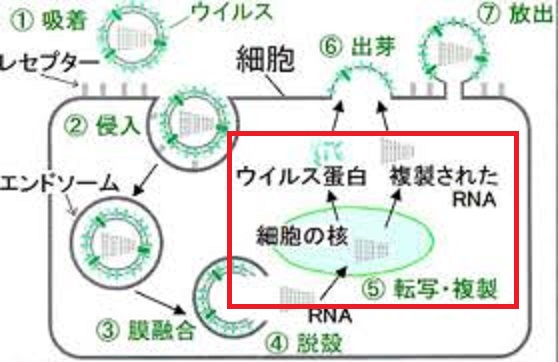
The HIV viral cycle. Step 1: the HIV fuses to the host-cell surface. Specifically, the gp120 proteins on the surface of the virus binds to the CD4. This then binds to a smaller coreceptor (CCR5 or CXCR4). Step 2: HIV RNA, reverse transtriptase, integrase, and other viral proteins enter the host cell. The virus is brought into the host cell and uncoated; both viral RNA and reverse transcriptase are loosed into the cell. Step 3: Viral DNA is formed by reverse transcription. Step 4: Viral DNA is transported across the nucleus and integrates into the host DNA. Integrase found on the viral DNA. The viral DNA in the host DNA is called provirus. Step 5: New viral RNA is used as genomic RNA and to make viral proteins. New viral RNA strands are made and leave the nucleus. Step 6: New viral RNA and proteins move to the cell surface and a new immature HIV forms. The viral is assembled in an outbulging of the host cell. Step 7: The virus matures when protease releases the proteins that form the mature HIV. Mature virion is released.
3D illustration Virus DNA molecule, structure. Concept destroyed code human genome. Damage DNA molecule

Whether a virus destroys the infected cell depends on the shape of the virus DNA, new research showed. Photo by Alex Evilevitch and Ting Liu

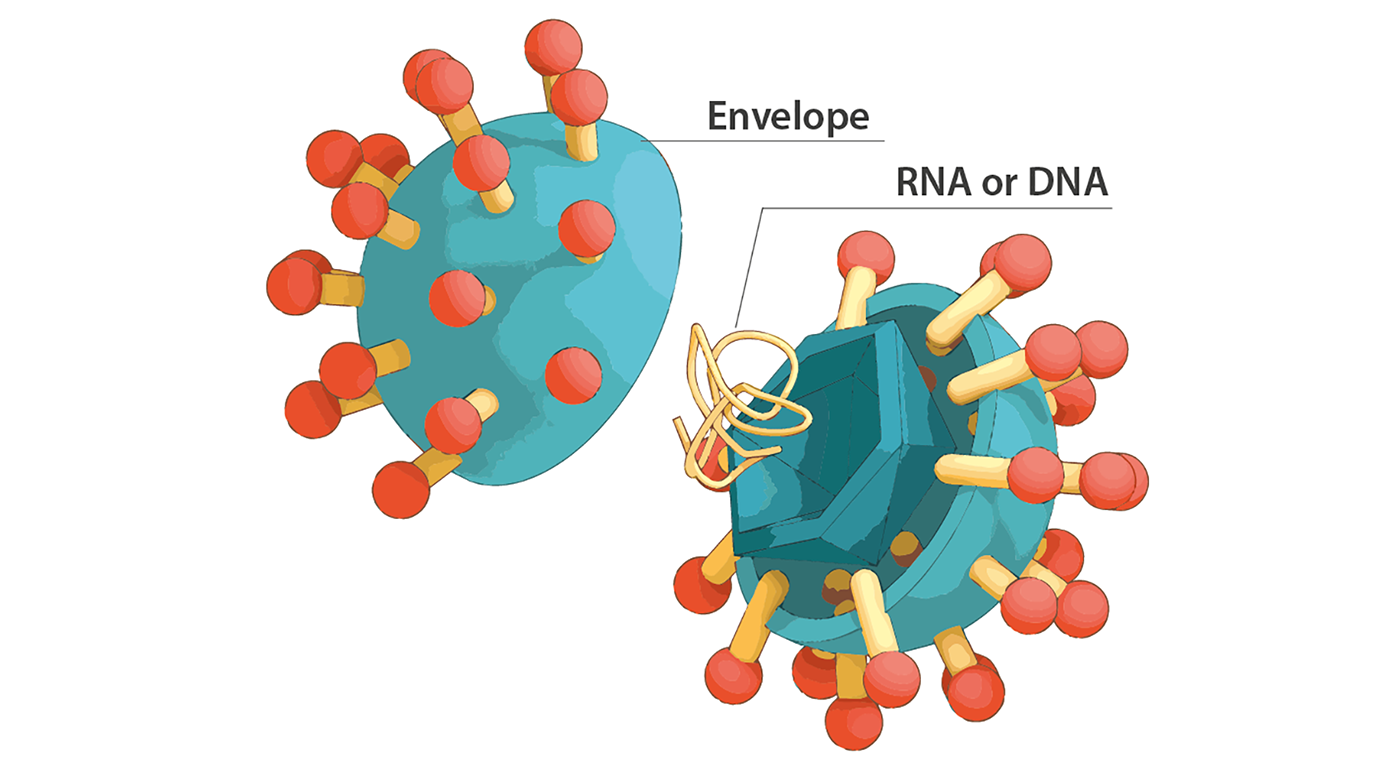
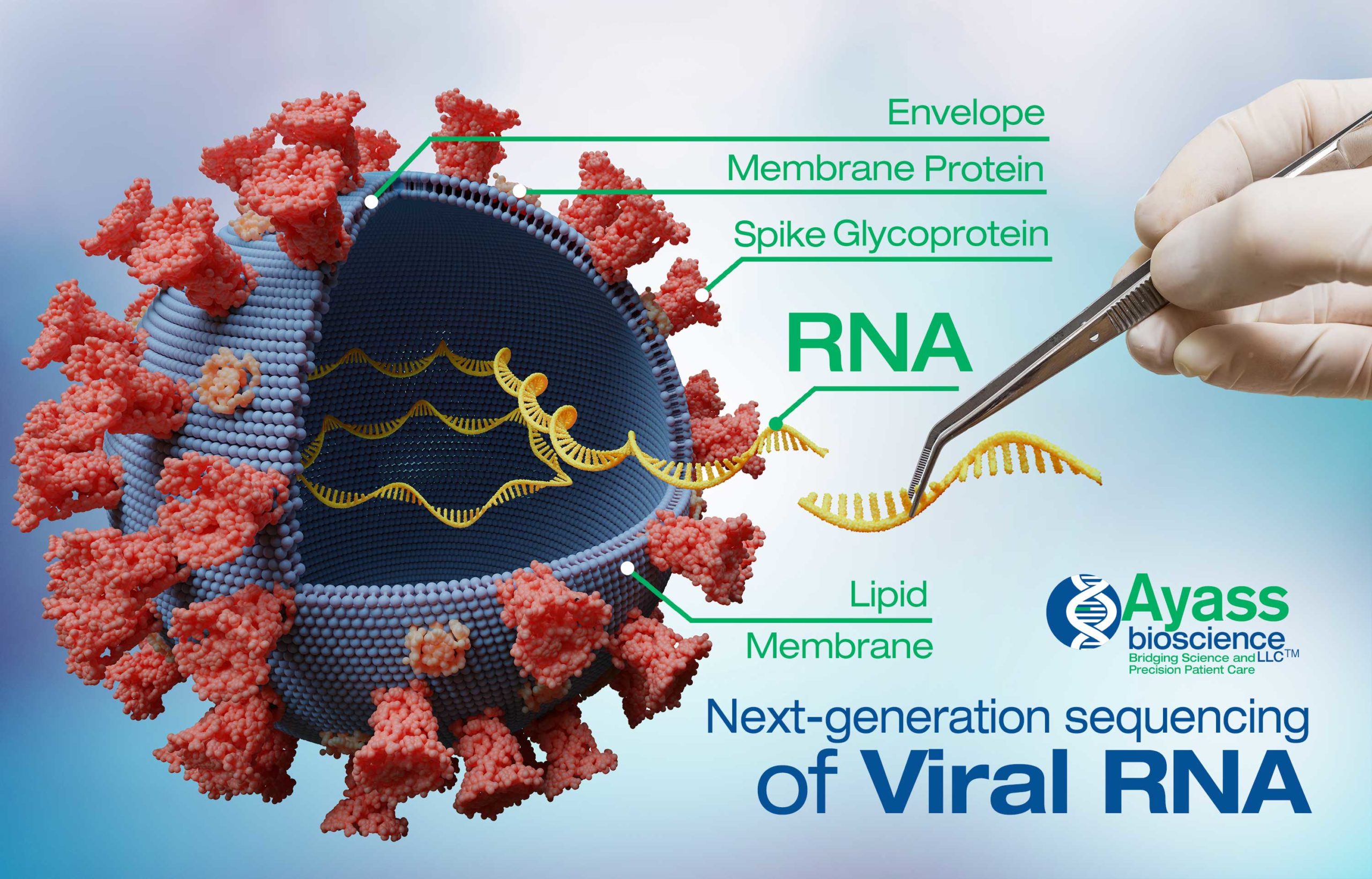
The virus structure is the set up of a virus. This includes nucleic acid, DNA or RNA. Nucleic Acid, Virus, Science, Peace Symbol, Google Images, Dna, Quick, Envelope

\12/25販売開始/【第92弾】【ウイスキーみくじ 466口限定】山崎18年 山崎12年 白州12年 響ジャパニーズハーモニー イチローズ 知多 など 福袋 酒くじ おみくじ ウイスキー くじ 最新
Human dna virus infection .Glowing neon DNA chain.Biotechnology, biochemistry, genetics and medicine concept.Vector

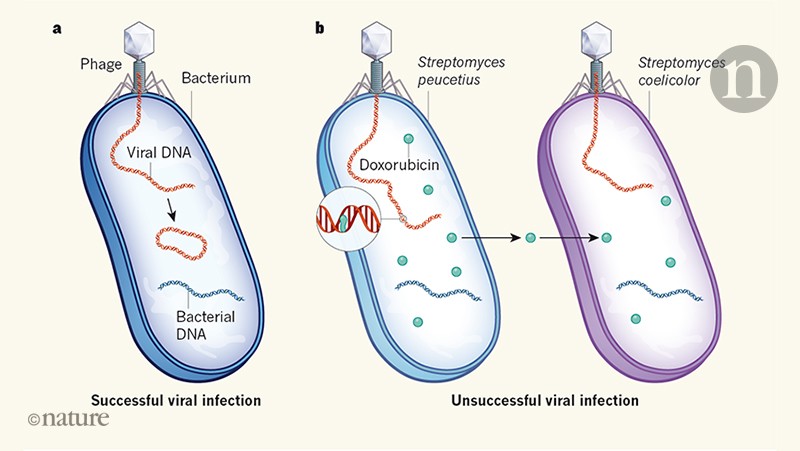
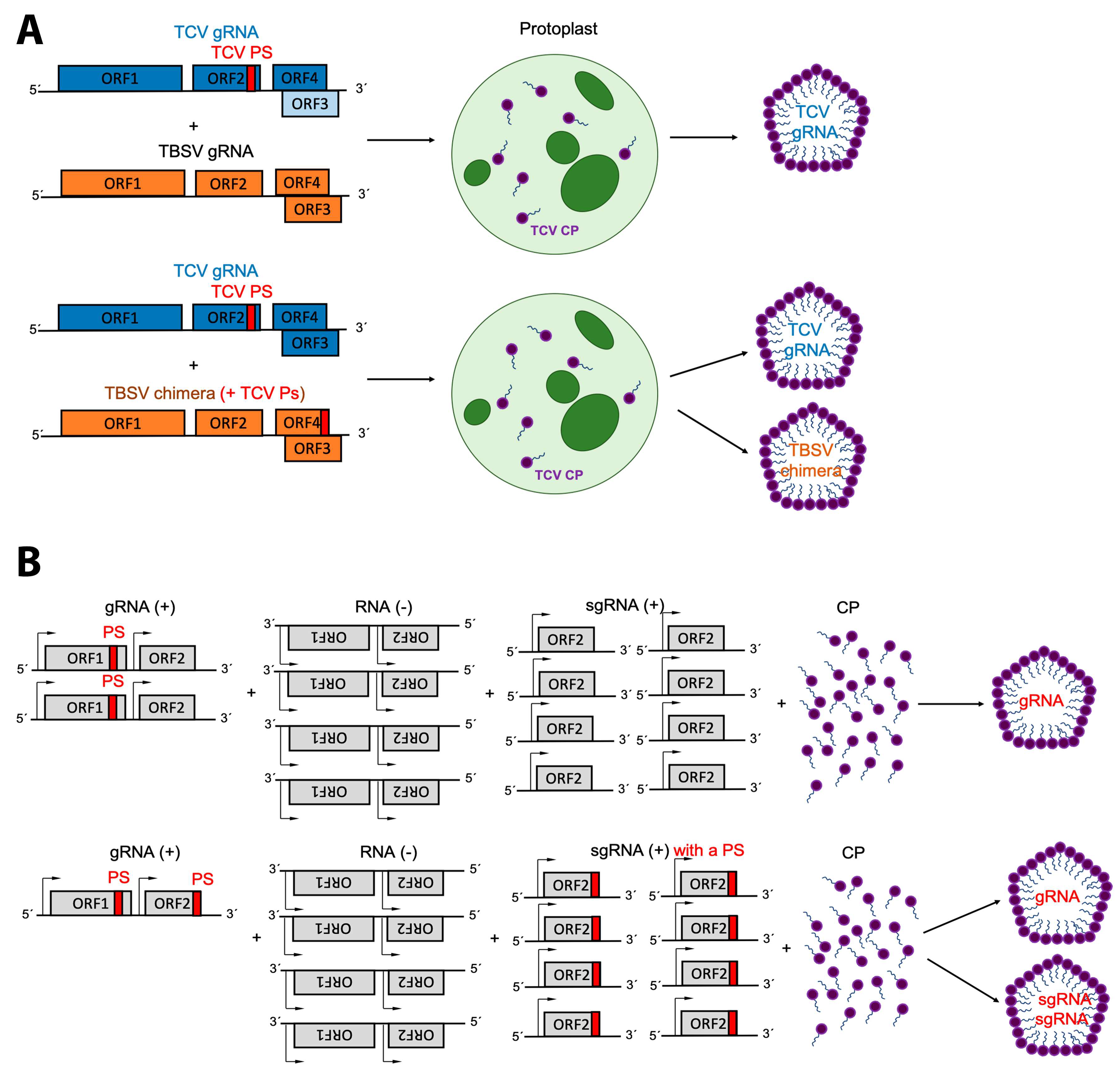
The steps of specialized transduction. Step 1 is viral attachment and penetration. This is when the phage infects a cell. This shows the virus sitting on the outside of a cell and injecting DNA into the cell. Step 2 is integration when the phage DNA becomes incorporated into the host genome. Step 3 is excisionwhen the phage is excised from the bacterial chromosomes along with a short piece of bacterial DNA. The DNA is then packaged into newly formed capsids. When the virus particles are assembled the DNA contains both viral and host segments. Step 4 is infection when the phage contains both viral and bacterial DNA infects a new host cell. Step 5 is recombination when the phage DNA along with the attached bacterial DNA are incorporated into a new cell. The image shows a new bacterial cell with virus DNA as well as other bacterial DNA in its genome.







![サッポロ ヱビス ビール 缶 350(350ml*24本入)【ヱビスビール】[ビール ギフト 贈り物]](https://thumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp/@0_mall/soukaidrink/cabinet/701/4901880916701.jpg?_ex=300x300)










![ブラックニッカクリア ペットボトル(4000ml*4本セット)【ブラックニッカ】[アサヒビール/ウイスキー/ブラックニッカ]](https://thumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp/@0_mall/soukaidrink/cabinet/734/540734.jpg?_ex=300x300)







![01/07(水)10時まで [元祖お酒くじ] 146限定 限定企画A127回 11000円で当たる 山崎 白州 響 イチローズモルト ウイスキー セット買いで飲み比べ ウイスキーくじ 酒くじ おみくじ くじびき 酒 お酒 くじ 福袋 日本酒くじ 焼酎くじ 日本酒 人気 おすすめ 最新 ギフト](https://thumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp/@0_mall/newyork001/cabinet/kuji-gentei-a106.jpg?_ex=300x300)