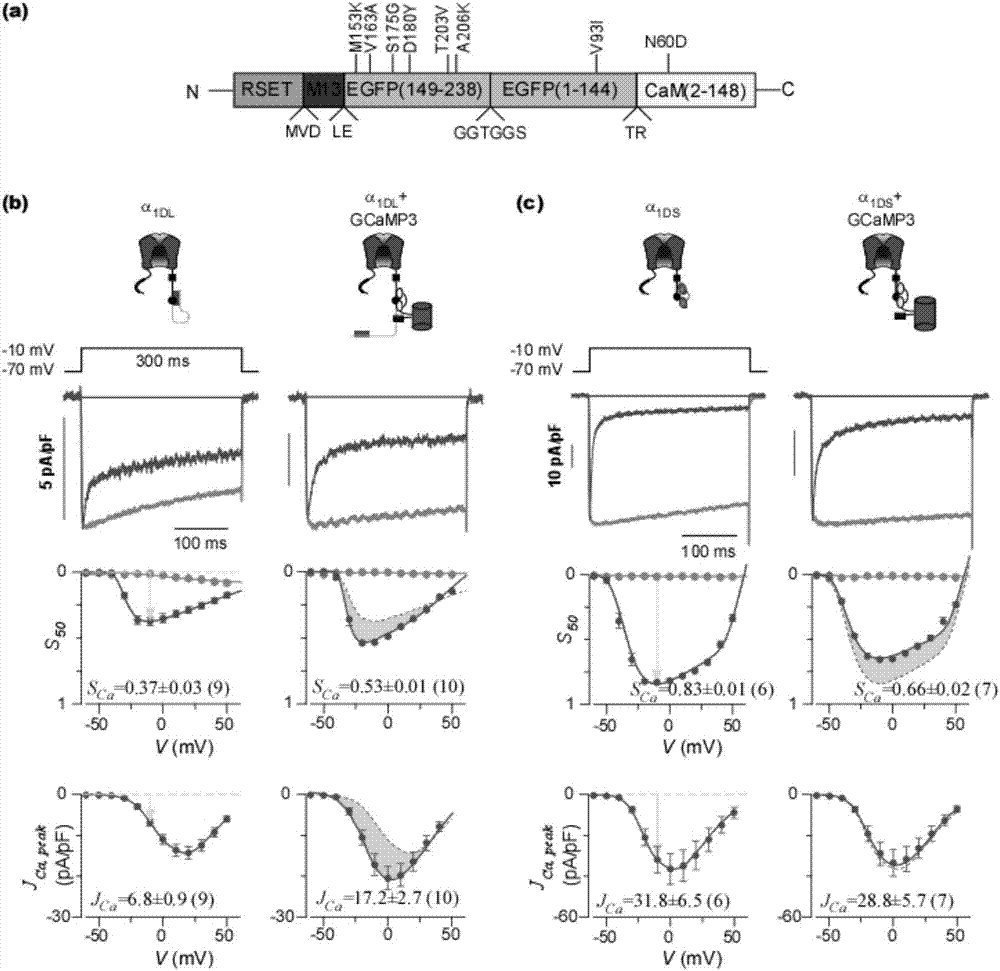
Images of GCaMP
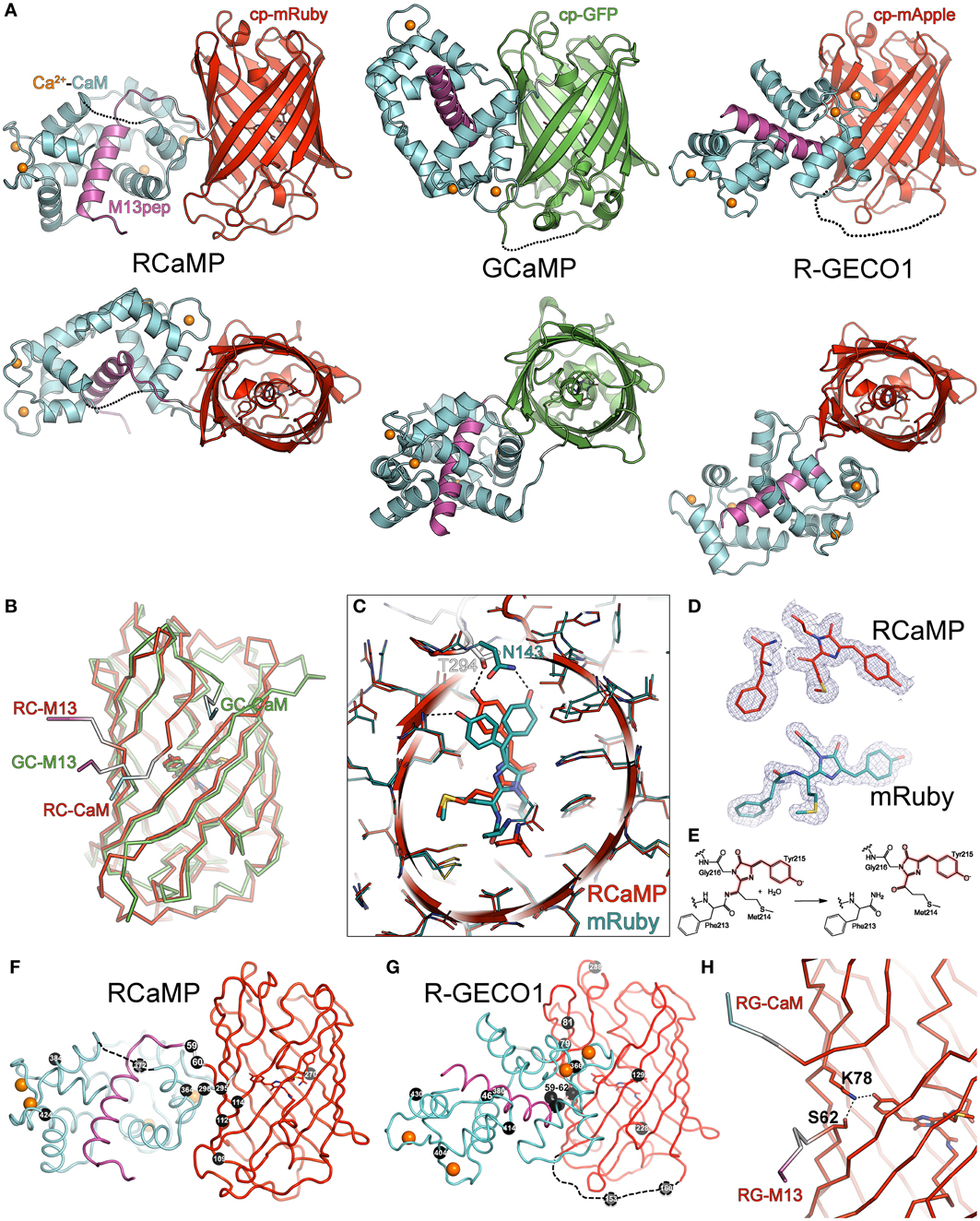
Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics

Unraveling Synaptic GCaMP Signals: Differential Excitability and Clearance Mechanisms Underlying Distinct Ca2+ Dynamics in Tonic and Phasic Excitatory, and Aminergic Modulatory Motor Terminals in Drosophila
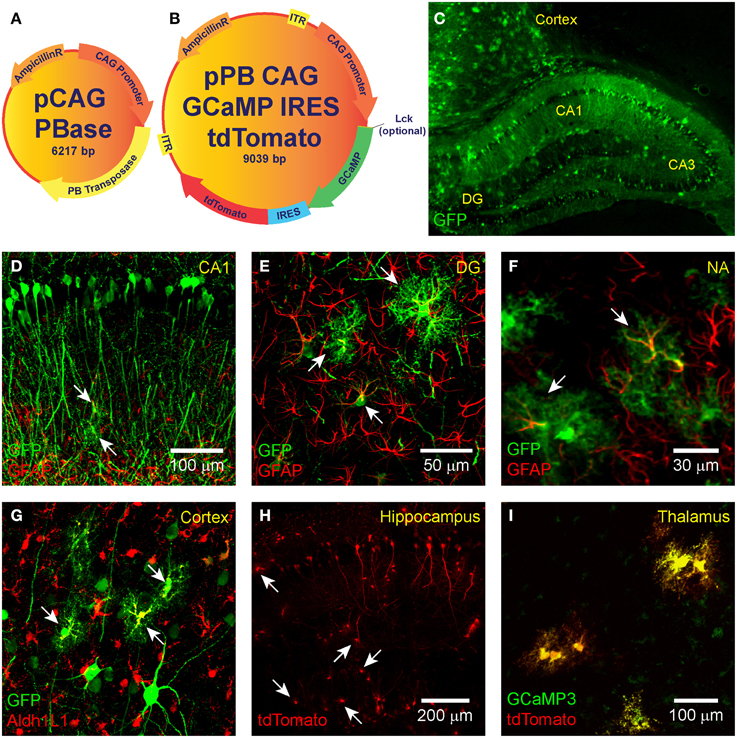
Imaging activity in astrocytes and neurons with genetically encoded calcium indicators following in utero electroporation
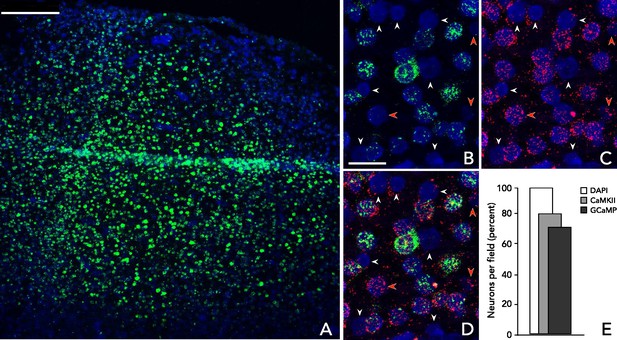
Calcium imaging with genetically encoded indicators in behaving primates Pupil size reflects activation of subcortical ascending arousal system nuclei during rest Loss of the extracellular matrix protein Perlecan disrupts axonal and synaptic stability during Drosophila development Male rodent perirhinal cortex, but not ventral hippocampus, inhibition induces approach bias under object-based approach-avoidance conflict

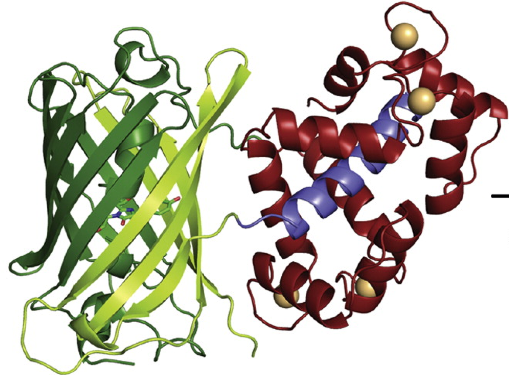




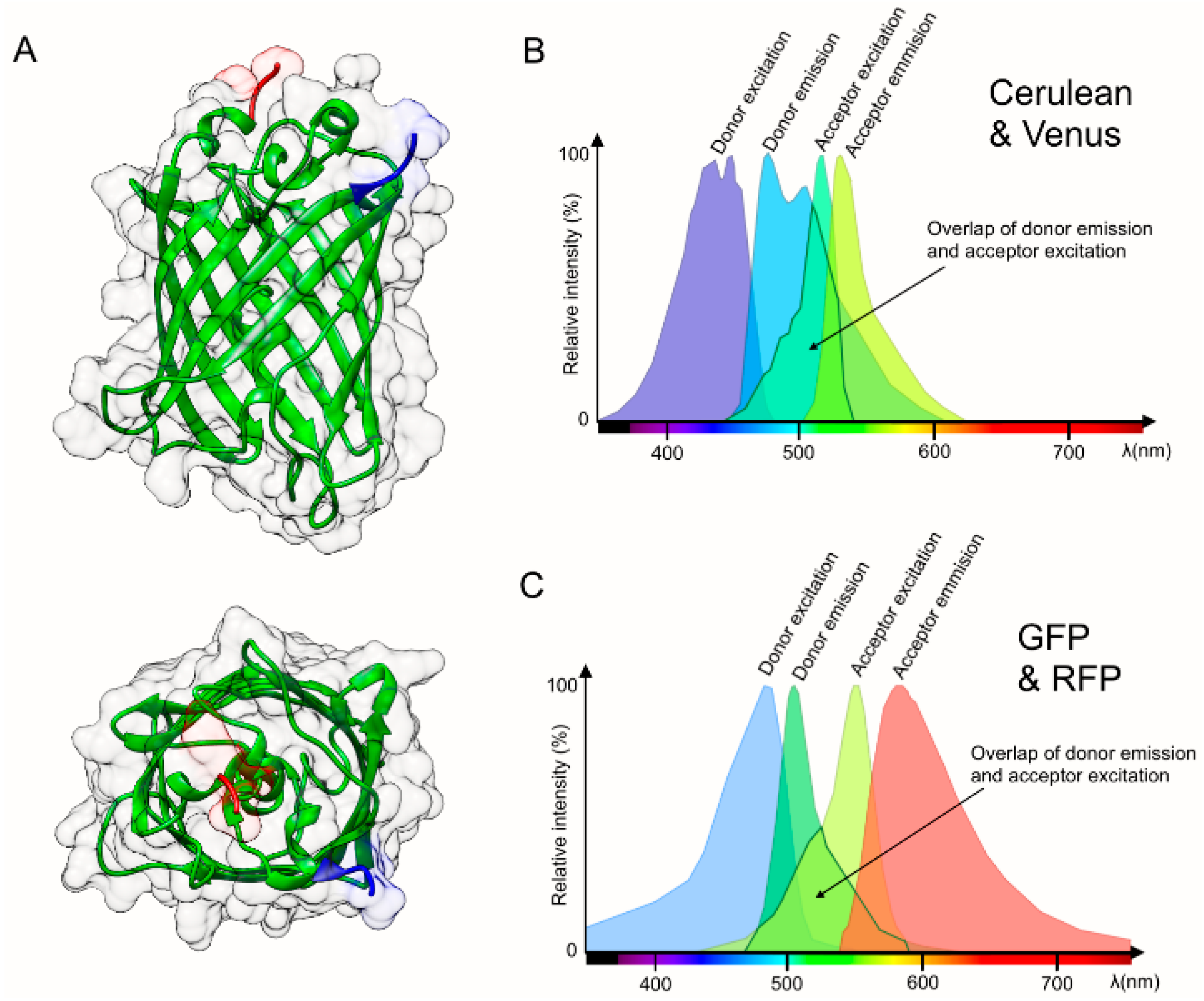
![サントリー 金麦 糖質75%オフ(350ml*48本)【金麦糖質オフ】[新ジャンル 第3のビール 発泡酒]](https://thumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp/@0_mall/soukaidrink/cabinet/867/63867.jpg?_ex=300x300)