Category:物理学のエポニム

フーコーの振り子
Foucault pendulum▲1 trends
ニュートンのゆりかご
Newton's cradle▲1 trends
ガル
Gal (unit)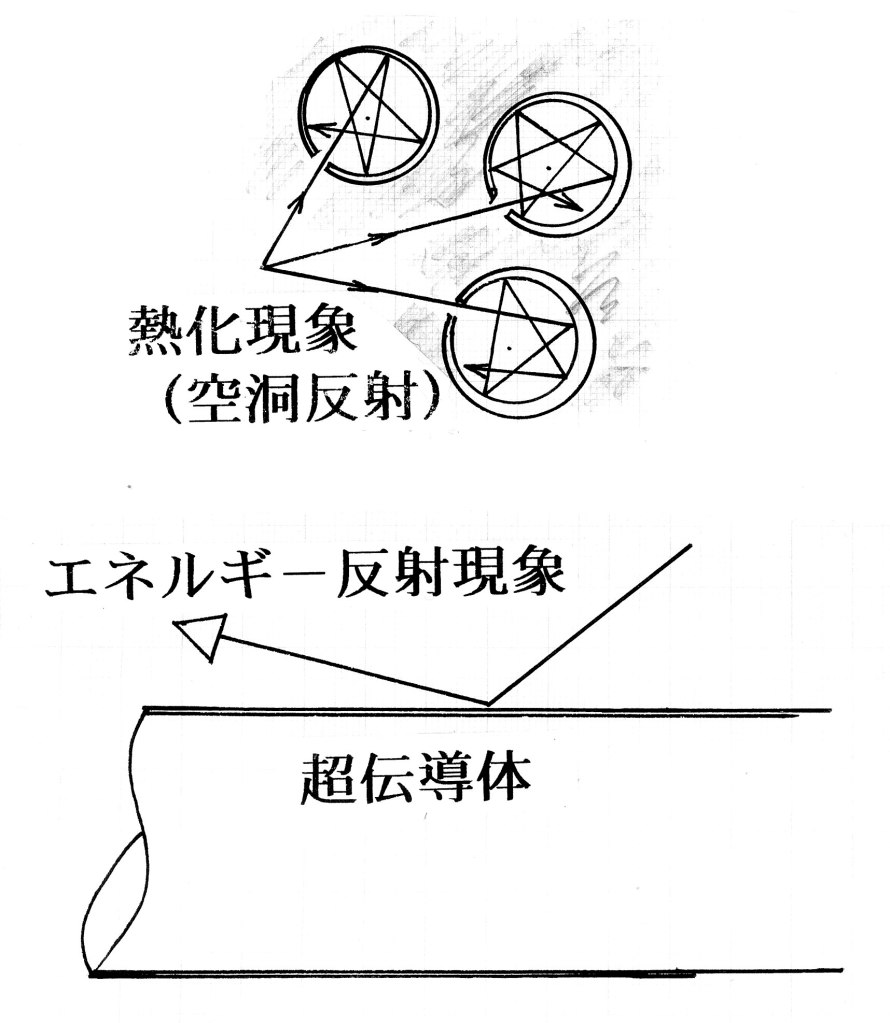
マイスナー効果
Meissner effectスターリングエンジン
Stirling engine
ウーの実験
Wu experiment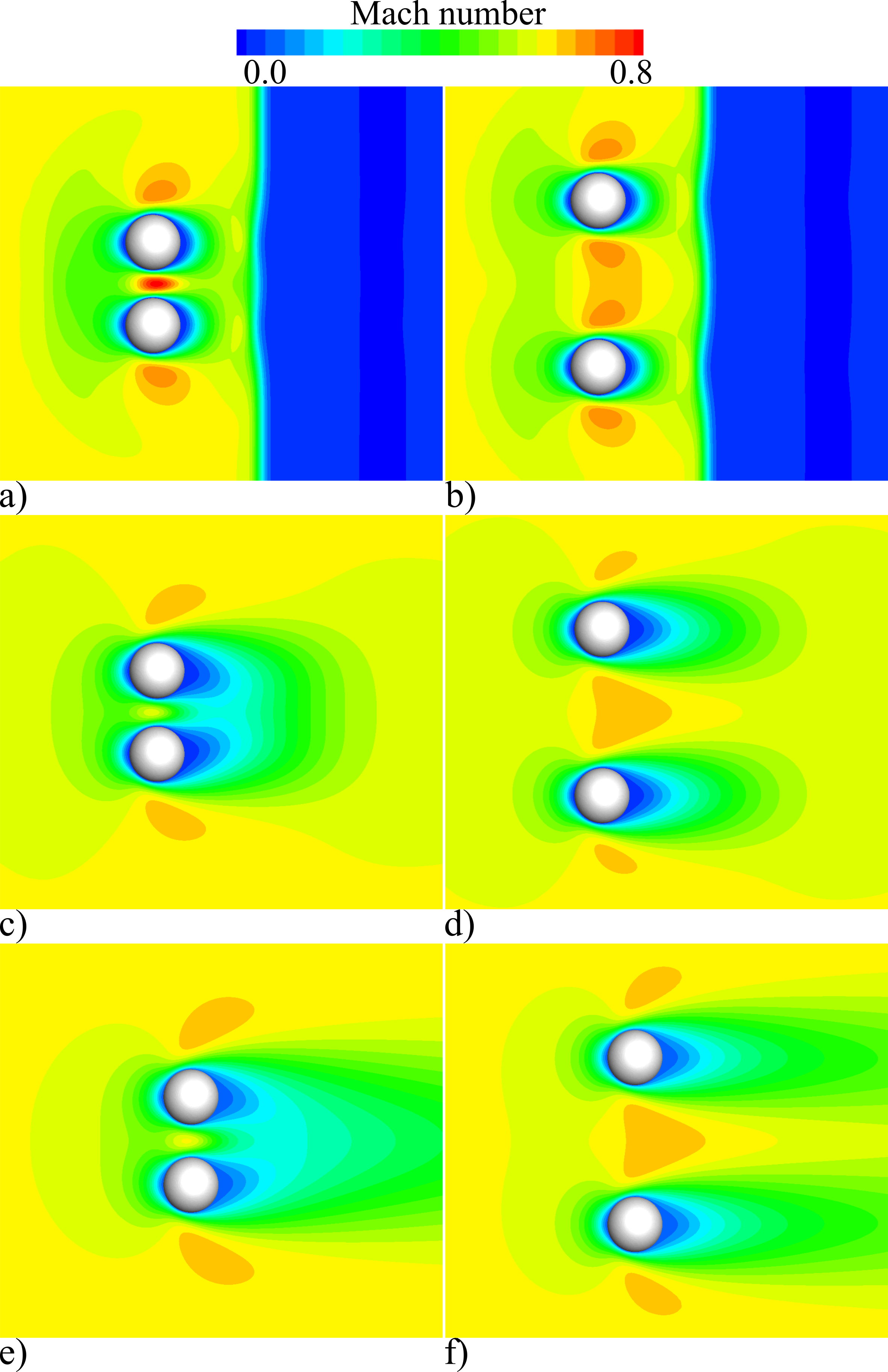
マッハ数
Mach number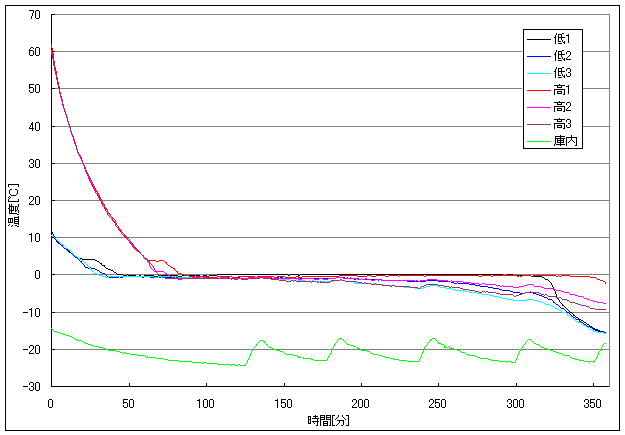
ムペンバ効果
Mpemba effect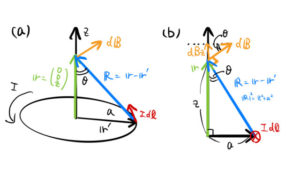
ビオ・サバールの法則
Biot–Savart law
キャヴェンディッシュの実験
Cavendish experiment
コアンダ効果
Coandă effect
久保公式
Kubo formula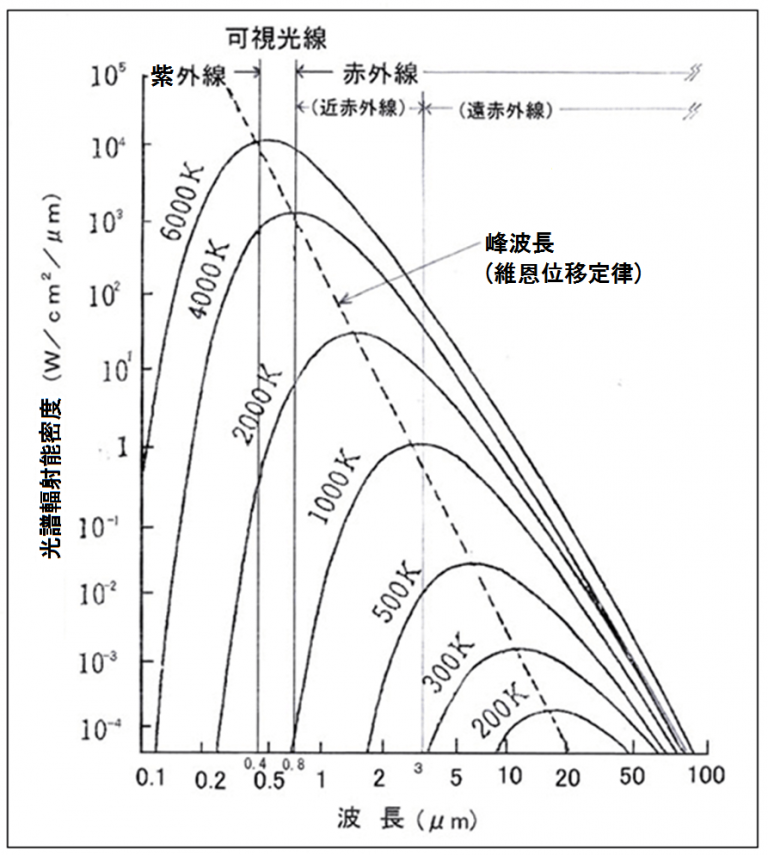
プランク温度
Planck temperature
ライデンフロスト効果
Leidenfrost effect
テスラコイル
Tesla coilシュワルツシルト半径
Schwarzschild radiusプランクの法則
Planck's law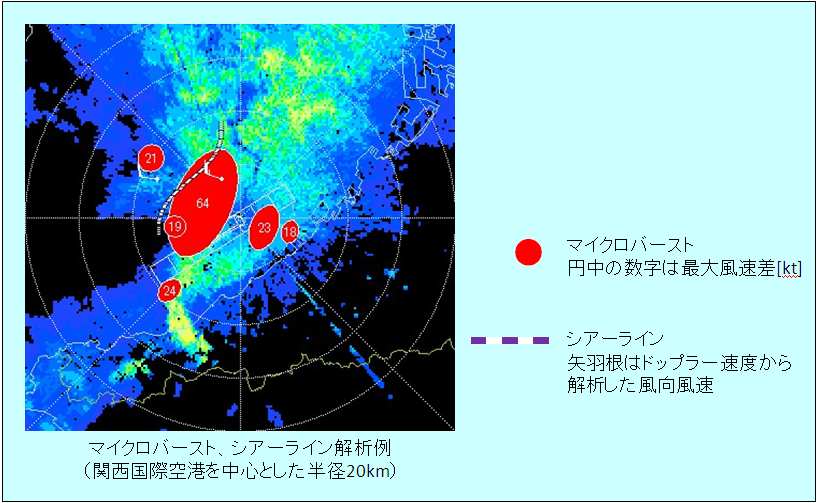
ドップラー・レーダー
Doppler radar
マイケルソン干渉計
Michelson interferometer
ラザフォード散乱
Rutherford scattering
フェルミ縮退
Degenerate matter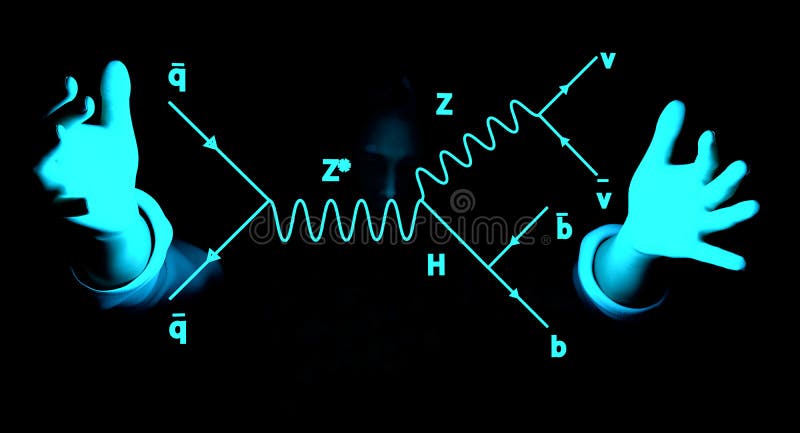
ファインマン・ダイアグラム
Feynman diagram
チンダル現象
Tyndall effect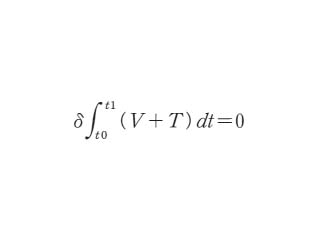
ハミルトン力学
Hamiltonian mechanics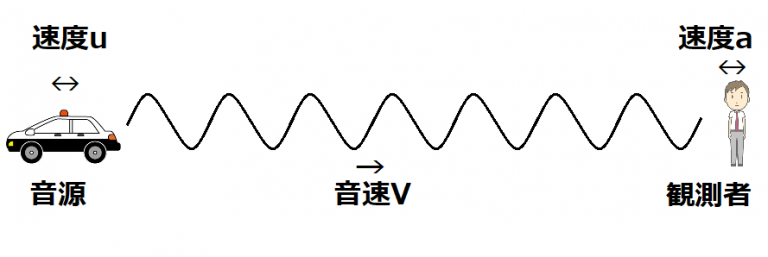
ドップラー効果
Doppler effect
フェルミ面
Fermi surface
修正ニュートン力学
Modified Newtonian dynamics
ウィーンの変位則
Wien's displacement law
