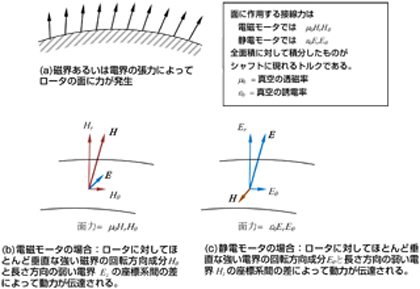
Category:自然科学の法則

アンペールの法則
Ampère's circuital law
運動の第2法則
Newton's second law
摩擦
Friction
ハーディー・ワインベルクの法則
Hardy–Weinberg principle
ティティウス・ボーデの法則
Titius–Bode law電磁場テンソル
Electromagnetic tensor
最小作用の原理
Action principles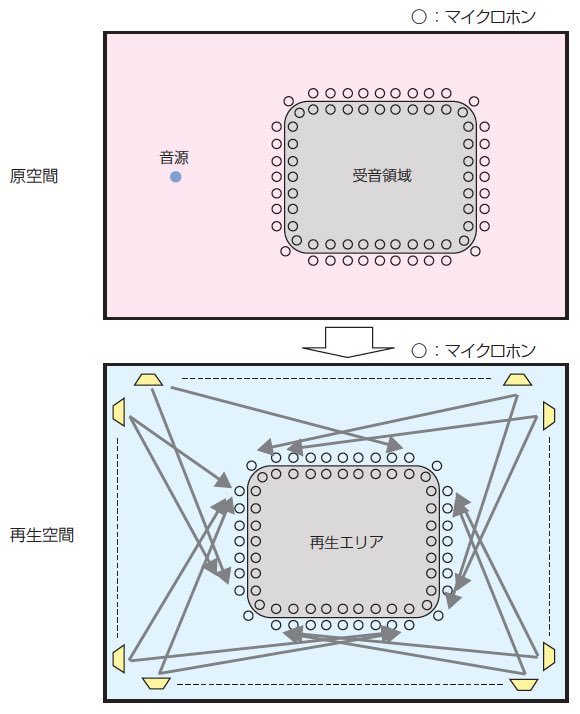
ホイヘンス=フレネルの原理
Huygens–Fresnel principle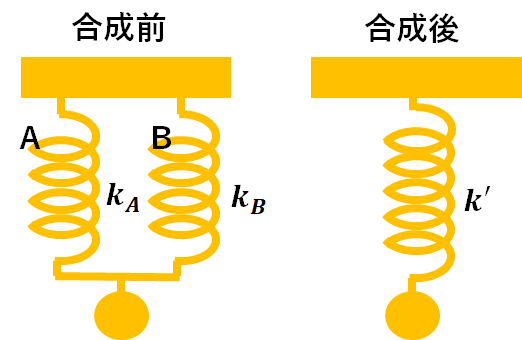
フックの法則
Hooke's law
質量とエネルギーの等価性
Mass–energy equivalence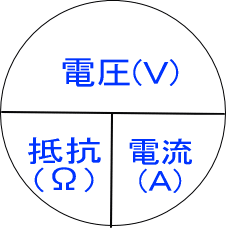
オームの法則
Ohm's law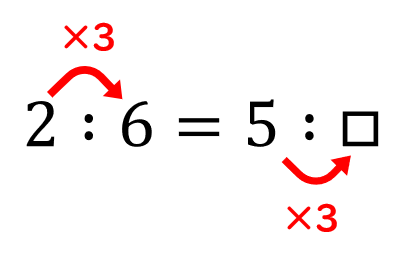
倍数比例の法則
Law of multiple proportions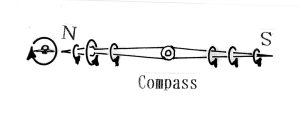
右ねじの法則

メンデルの法則
Mendelian inheritance
保存則
Conservation law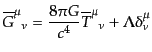
アインシュタイン方程式
Einstein field equations
運動量保存則
Conservation of momentum
ヒューム‐ロザリーの法則
Hume-Rothery rules
ファラデーの電磁誘導の法則
Faraday's law of induction
デリャーギン・ランダウ・フェルウェー・オーバービーク理論
DLVO theory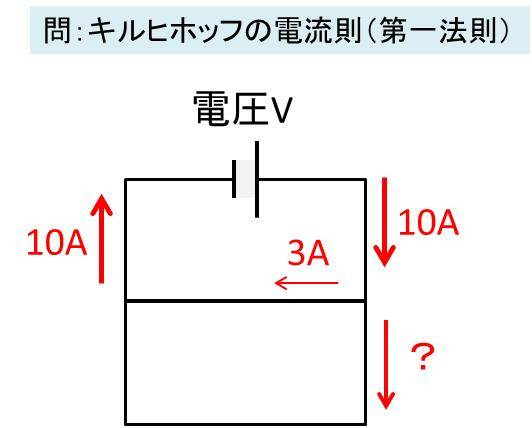
分流の法則
Current divider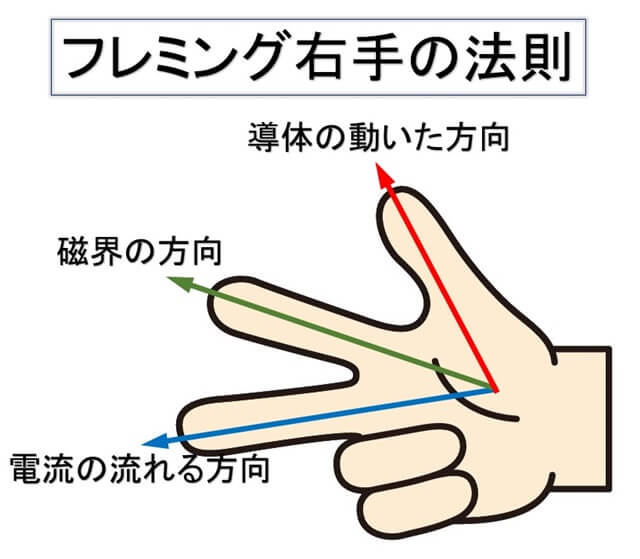
右手の法則
Right-hand rule
地層累重の法則
Law of superposition
グレアムの法則
Graham's law
フレミングの左手の法則
Fleming's left-hand rule for motors
テレゲンの定理
Tellegen's theorem
ヘンリーの法則
Henry's law
オームの音響法則
Ohm's acoustic law