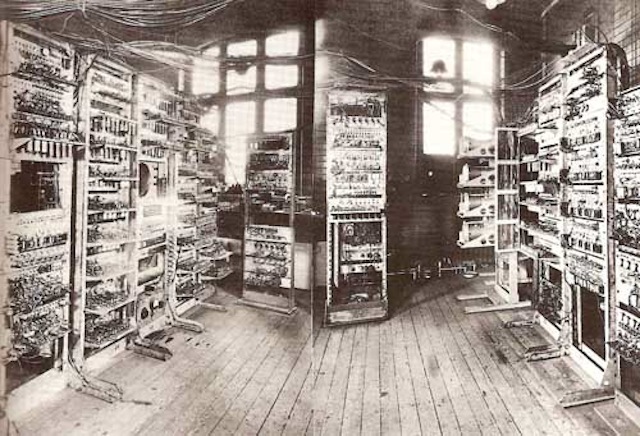
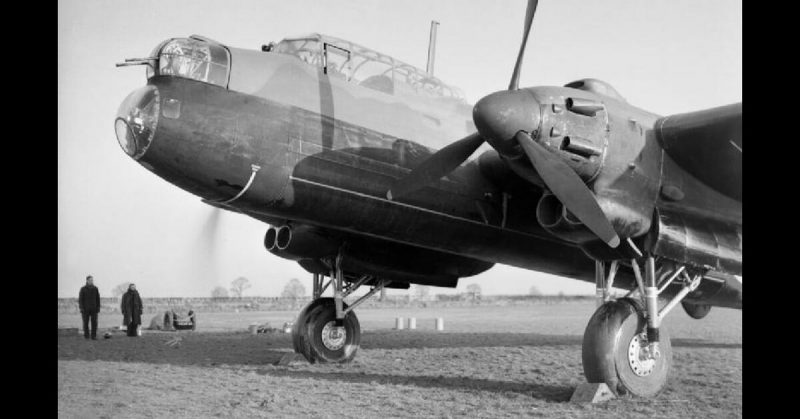
Images of Manchester Mark I

manchester-mark-1+Turing small_art_full I Love Manchester, University Of Manchester, Alan Turing, Alter Computer, Bletchley Park, Deep Time, The Imitation Game, Old Computers, Story Of The World
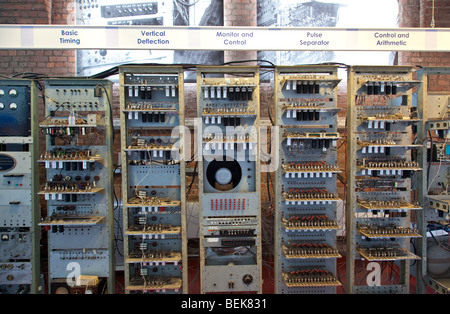
Manchester Mark 1 erste gespeicherte Programm Computer im Museum of Science and Industry (MOSI), Liverpool Straße, Manchester UK

Avro Manchester Mark I, L7284 EM-D, of No. 207 Squadron RAF based at Waddington, Lincolnshire, in flight. Navy Aircraft, Wwii Aircraft, Raf Bases, Air Force Bomber, Wwii Plane, Waddington, Vintage Aircraft, Royal Air Force, War Machine

Manchester Mark 1 premier ordinateur à programme enregistré au Musée des sciences et de l'industrie (MOSI), Liverpool, Manchester UK
![Historia de la informática 3000 A.C Ábaco Varillas de John Napier para calcular Reglas de cálculo (William Oughtred) Máquina de Pascal: Pascalina Máquina de Leibnitz Telares Jacquard Arithmometer Máquina diferencial de Charles Babbage Máquina analítica de Charles Babbage Máquina tabuladota de Hollerith para el Censo de EE.UU Ajedrez automático de Leonardo Torres Quevedo Z1, de Conrad Zuse (Alemania) Hp Harvard Mark I, de Howard Aiken (EE.UU)= IBM Automatic Sequence Control Calculator [ASCC] ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer) Manchester Mark I Whirlwind (Jay Forrester, MIT) EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer) ILLIAC I DEC: Digital Equipment Corporation DEC PDP-1 DEC PDP-8 Burroughs B2500 y B3500 Cray-1](https://s3.amazonaws.com/s3.timetoast.com/public/uploads/photos/7231820/dai-tommy.jpg)
Historia de la informática 3000 A.C Ábaco Varillas de John Napier para calcular Reglas de cálculo (William Oughtred) Máquina de Pascal: Pascalina Máquina de Leibnitz Telares Jacquard Arithmometer Máquina diferencial de Charles Babbage Máquina analítica de Charles Babbage Máquina tabuladota de Hollerith para el Censo de EE.UU Ajedrez automático de Leonardo Torres Quevedo Z1, de Conrad Zuse (Alemania) Hp Harvard Mark I, de Howard Aiken (EE.UU)= IBM Automatic Sequence Control Calculator [ASCC] ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer) Manchester Mark I Whirlwind (Jay Forrester, MIT) EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer) ILLIAC I DEC: Digital Equipment Corporation DEC PDP-1 DEC PDP-8 Burroughs B2500 y B3500 Cray-1

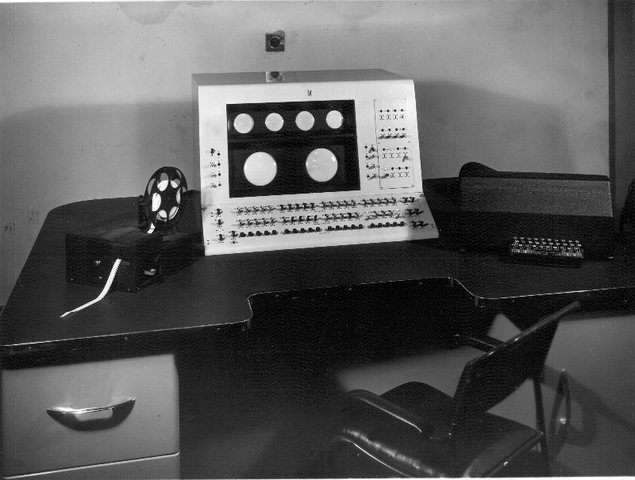
The Progression of the Computer Hewlett-Packard Founded First Bombe Completed Complex NUmber Calculator Presented Z3 Computer Completed Project Whirlwind Begins Harvard Mark-1 is Completed First Colossus is Operational John von Neumann wrote "First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC" ENIAC Made Public EDSAC Assembled Manchester Mark I SEAC ERA 1101 Lyons Electronic Office IAS Computer Operational IBM Ships First Electronic Computer IBM 650 TX-0 SAGE 7000 Series Mainframes DEC´s PDP-1 81.2-% Share LINC System/360 6600 Supercomputer PDP-8 Apollo Guidance Computer Nova Kenbak-1 HP-35 TV Typewriter Micral 8H Computer Alto VDM Prototype Altair 8800 Tandem-16 Apple-1 Apple II Commodore PET TRS-80 Model 400 Computer DN100 Osborne I Commodore 64 PC clone Macintosh PC-AT Amiga 1000 Artificial Intelligence Jump PS/2 VAX 11/780 NeXT The Atanasoff-Berry Computer is Completed ILLIAC IV HP-2115

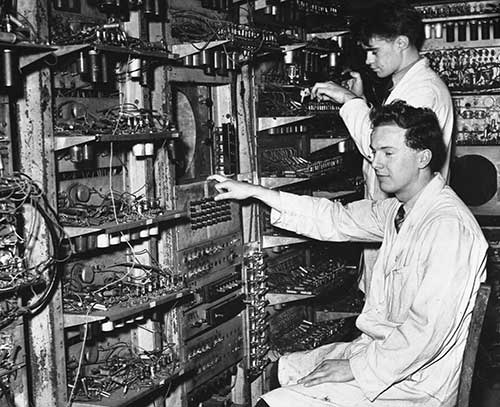
A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence Al-Jazari created a programmable orchestra of mechanical human beings Blaise Pascal invented the mechanical calculator, the first digital calculating machine Leonardo Torres y Quevedo built a chess automaton Konrad Zuse built the first working program-controlled computer Isaac Asimov published his Three Laws of Robotics The first working AI programs were written in 1951 to run on the Ferranti Mark 1 machine of the University of Manchester: a checkers-playing program written by Christopher Strachey and a chess-playing program written by Dietrich Prinz. The General Problem Solver (GPS) demonstrated by Newell, Shaw and Simon. Edward Feigenbaum invented Dendral, software made to deduce the molecular structure of organic compounds using scientific instrument data. It was the first expert system. Ian Horswill extended behavior-based robotics by creating Polly, the first robot to navigate using vision and operate at animal-like speeds The Deep Blue chess machine defeats the then world chess champion, Garry Kasparov. First official RoboCup football (soccer) match featuring table-top matches with 40 teams of interacting robots and over 5000 spectators. Honda's ASIMO robot, an artificially intelligent humanoid robot, is able to walk as fast as a human, delivering trays to customers in restaurant settings. Google builds self driving car Apple's Siri, Google's Google Now and Microsoft's Cortana are smartphone apps that use natural language to answer questions, make recommendations and perform actions.



11508864067835_large.jpg)
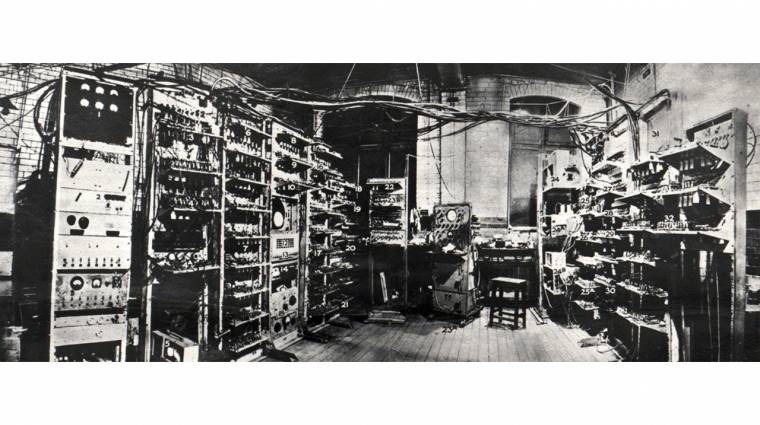




















![[プレミアリーグ] マンチェスターシティ シンプル ロゴスマホ壁紙画像 2017/08/18](https://cdn.amebaowndme.com/madrid-prd/madrid-web/images/sites/298387/164ecc7a39a44d5a47dadf1363944a6a_0e3224f6ac61bdc408f93771ed461bf7.jpg)


















