Category:物理学のエポニム

クーロン爆発
Coulomb explosion▲1 trends
シュレーディンガーの猫
Schrödinger's cat▲2 trends
ラグランジュ点
Lagrange point▲1 trends
ケルビン
Kelvin▲1 trends
フーコーの振り子
Foucault pendulum▲1 trends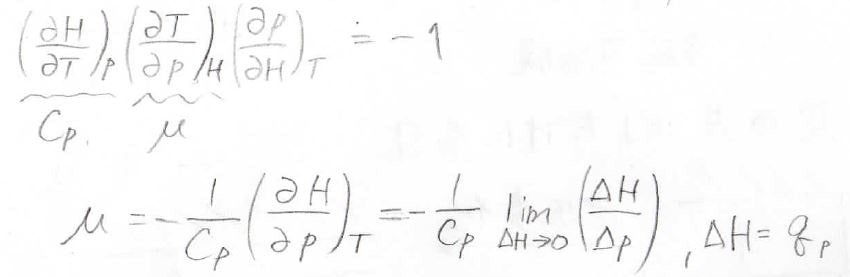
ジュール=トムソン効果
Joule–Thomson effect
ドルーデモデル
Drude model
コッククロフト・ウォルトン回路
Cockcroft–Walton generator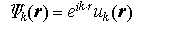
ブロッホの定理
Bloch's theorem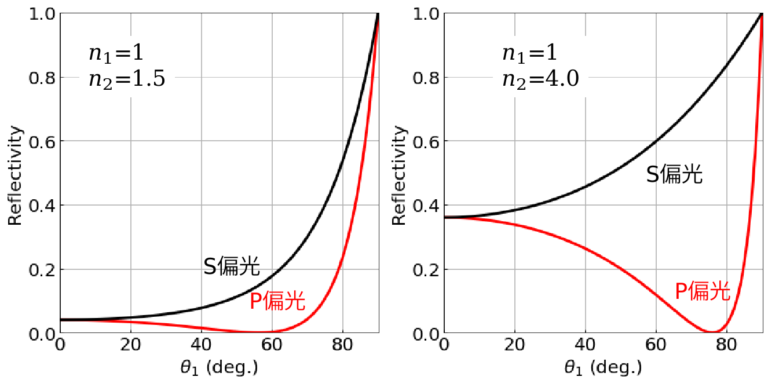
ファラデー効果
Faraday effect
ブレイトンサイクル
Brayton cycle
アンペールの法則
Ampère's circuital law
ドップラー効果
Doppler effect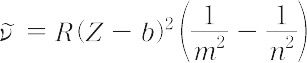
ボーアの原子模型
Bohr model
シュレディンガー音頭

アインシュタイン=ポドルスキー=ローゼンのパラドックス
Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
ウィーデマン・フランツの法則
Wiedemann–Franz law
ボーム解釈
De Broglie–Bohm theory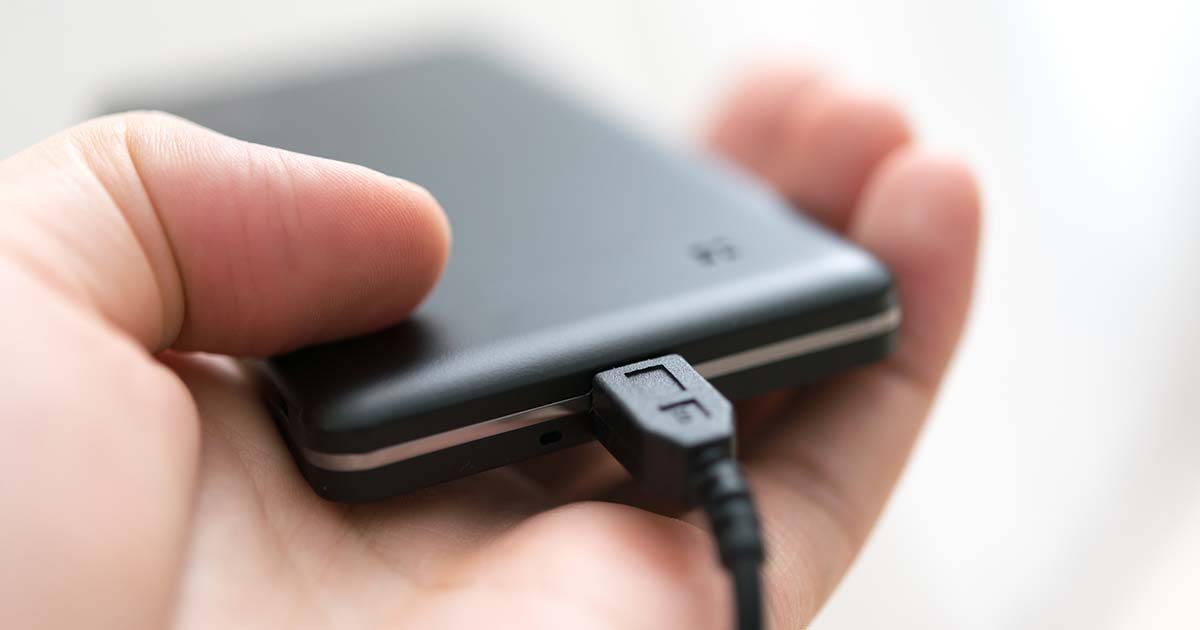
アンペア
Ampereボース分布関数
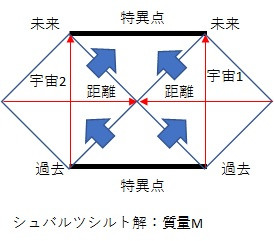
Bose–Einstein statisticsシュワルツシルト解
Schwarzschild metric
フェルミエネルギー
Fermi energy
ホール効果
Hall effect
ボーア磁子
Bohr magneton
ジュールの法則
Joule's first law
サニャック効果
Sagnac effect
コペルニクスの原理
Copernican principle
テラヘルツ